Discover Your Ideal Phone
with Phone.ma
iPAQ Glisten
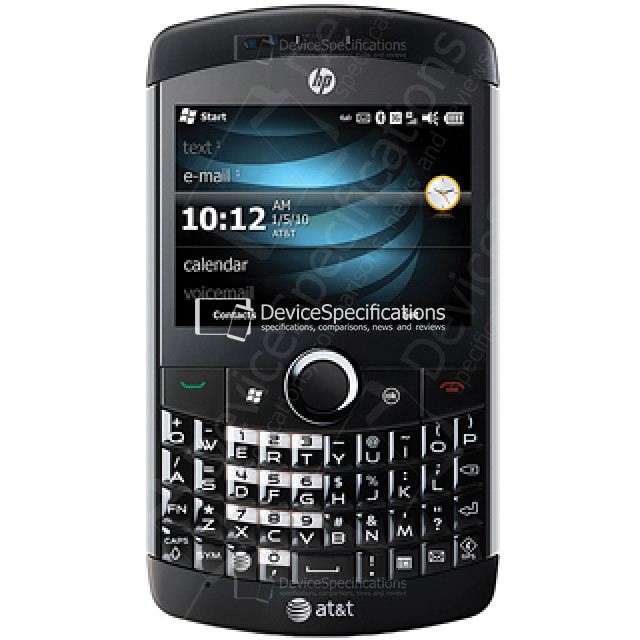

Description
Weight: 132 g
SoC: Qualcomm MSM7200
CPU: ARM1136EJ-S, 400 MHz, Cores: 1
RAM: 256 MB
Memory cards: microSD, microSDHC
Display: 2.5 in, AMOLED, 320 x 240 pixels, 18 bit
Battery: 1590 mAh, Li-Polymer
OS: Microsoft Windows Mobile 6.5 Professional
Camera: 2048 x 1536 pixels, 320 x 240 pixels
SIM card: Mini-SIM
Wi-Fi: b, g
USB: 2.0, Micro USB
Bluetooth: 2.0
Positioning: GPS, A-GPS
Brand and model
Information about the brand, model and model alias (if any) of a specific device.
| Brand Brand name of the company that manufactures the device. | HP |
| Model Model name of the device. | iPAQ Glisten |
| Model alias Аlternative names, under which the model is known. | iPAQ K3 Obsidian Pegatron Obsidian iPAQ KB1 |
Design
Information about the dimensions and weight of the device, shown in different measurement units. Body materials, available colors, certifications.
| Width Information about the width, i.e. the horizontal side of the device when it is used in its standard orientation. | 62.8 mm (millimeters) 6.28 cm (centimeters) 0.206 ft (feet) 2.472 in (inches) |
| Height Information about the height, i.e. the vertical side of the device when it is used in its standard orientation. | 112.8 mm (millimeters) 11.28 cm (centimeters) 0.37 ft (feet) 4.441 in (inches) |
| Thickness Information about the thickness/depth of the device in different measurement units. | 13.4 mm (millimeters) 1.34 cm (centimeters) 0.044 ft (feet) 0.528 in (inches) |
| Weight Information about the weight of the device in different measurement units. | 132 g (grams) 0.29 lbs (pounds) 4.66 oz (ounces) |
| Volume Estimated volume of the device, calculated from the dimensions provided by the manufacturer. Applies for devices in the form of a rectangular parallelepiped. | 94.92 cm³ (cubic centimeters) 5.76 in³ (cubic inches) |
SIM card
The Subscriber Identity Module (SIM) is used in mobile devices for storing data authenticating the subscribers of mobile services.
| SIM card type Information about the type and size (form factor) of the SIM card used in the device. | Mini-SIM (2FF - second form factor, since late 1990s, 25.00 x 15.00 x 0.76 mm) |
| Number of SIM cards Information about the number of SIM cards, supported by the device. | 1 |
Networks
A mobile (cellular) network is a radio system, which allows a large number of mobile devices to communicate with each other.
| GSM GSM (Global System for Mobile Communications) was developed to replace the analog cellular network (1G), therefore it is referred to as a 2G mobile network. It has been improved with the addition of General Packet Radio Services (GPRS) and later via the Enhanced Data rates for GSM Evolution (EDGE) technology. | GSM 850 MHz GSM 900 MHz GSM 1800 MHz GSM 1900 MHz |
| UMTS UMTS stands for Universal Mobile Telecommunications System. Based on the GSM standard, it is deemed as a 3G mobile network standard. It has been developed by the 3GPP and its major advantage is the provision of greater bandwidth and spectral efficiency, due to the W-CDMA technology. | UMTS 900 MHz UMTS 1900 MHz UMTS 2100 MHz |
Mobile network technologies and bandwidth
Communication between devices within mobile networks is realized via various generations of network technologies, which provide different bandwidth.
| Mobile network technologies There are several network technologies that enhance the performance of mobile networks mainly by increased data bandwidth. Information about the communication technologies supported by the device and their respective uplink and downlink bandwidth. | UMTS (384 kbit/s ) EDGE Class 10 (59.2-118.4 kbit/s , 177.6-236.8 kbit/s ) GPRS Class 10 (16-24 kbit/s , 32-48 kbit/s ) HSPA (HSDPA 7.2 Mbit/s ) |
Operating system
Operating system is the system software, which manages and controls the functioning of the hardware components of the device.
| Operating system (OS) Information about the operating system used by the device as well as its version. | Microsoft Windows Mobile 6.5 Professional |
System on Chip (SoC)
A system on a chip (SoC) includes into a single chip some of the main hardware components of the mobile device.
| SoC The SoC integrates different hardware components such as the CPU, GPU, memory, peripherals, interfaces, etc., as well as software for their functioning. | Qualcomm MSM7200 |
| Process technology Information about the process technology used in manufacturing the chip. The value in nanometers represents half the distance between elements that make up the CPU. | 90 nm (nanometers) |
| CPU CPU is the Central Processing Unit or the processor of a mobile device. Its main function is to interpret and execute instructions contained in software applications. | ARM1136EJ-S |
| CPU bits The CPU bits are determined by the bit-size of the processor registers, address buses and data buses. 64-bit CPUs provide better performance than 32-bit ones, which on their part perform better than 16-bit processors. | 32 bit |
| CPU cores A CPU core is the processor unit, which executes software instructions. Presently, besides single-core processors, there are dual-core, quad-core, hexa-core and so on multi-core processors. They increase the performance of the device allowing the execution of multiple instructions in parallel. | 1 |
| CPU frequency The frequency of the processor describes its clock rate in cycles per second. It is measured in Megahertz (MHz) or Gigahertz (GHz). | 400 MHz (megahertz) |
| RAM capacity RAM (Random-Access Memory) is used by the operating system and all installed applications. Data in the RAM is lost after the device is turned off or restarted. | 256 MB (megabytes) |
| RAM type Information about the type of RAM used by the device. | SDRAM |
| ROM capacity ROM is a type of permanent data storage, from which data can only by read and not edited. In some mobile devices this is the internal memory, which stores the OS. ROM is used mainly to store non-volatile data and program code, which is saved even if the power is off. | 512 MB (megabytes) 524288 KB (kilobytes) |
Memory cards
Memory cards are used in mobile devices for expanding their external storage capacity.
| Types The various types of memory cards are characterized by different sizes and capacity. Information about the supported types of memory cards. | microSD microSDHC |
Display
The display of a mobile device is characterized by its technology, resolution, pixel density, diagonal length, color depth, etc.
| Type/technology One of the main characteristics of the display is its type/technology, on which depends its performance. | AMOLED |
| Diagonal size In mobile devices display size is represented by the length of its diagonal measured in inches. | 2.5 in (inches) 63.5 mm (millimeters) 6.35 cm (centimeters) |
| Width Approximate width of the display | 2 in (inches) 50.8 mm (millimeters) 5.08 cm (centimeters) |
| Height Approximate height of the display | 1.5 in (inches) 38.1 mm (millimeters) 3.81 cm (centimeters) |
| Aspect ratio The ratio between the long and the short side of the display | 1.333:1 4:3 |
| Resolution The display resolution shows the number of pixels on the horizontal and vertical side of the screen. The higher the resolution is, the greater the detail of the displayed content. | 320 x 240 pixels |
| Pixel density Information about the number of pixels per centimeter (ppcm) or per inch (ppi) of the display. The higher the pixel density, the more detailed and clearer is the information displayed on the screen. | 160 ppi (pixels per inch) 62 ppcm (pixels per centimeter) |
| Color depth The color depth of the display is also known as bit depth. It shows the number of bits used for the color components of one pixel. Information about the maximum number of colors the screen can display. | 18 bit 262144 colors |
| Display area The estimated percentage of the screen area from the device's front area. | 27.41 % (percent) |
| Other features Information about other functions and features of the display. | Resistive |
Sensors
Different sensors measure different physical quantities and convert them into signals recognizable by the mobile device.
| Sensors Sensors vary in type and purpose. They increase the overall functionality of the device, in which they are integrated. | Proximity Light |
Rear camera
The primary camera of the mobile device is usually placed on its back and can be combined with one or more additional cameras.
| Image resolution One of the main characteristics of the cameras is their image resolution. It states the number of pixels on the horizontal and vertical dimensions of the image, which can also be shown in megapixels that indicate the approximate number of pixels in millions. | 2048 x 1536 pixels 3.15 MP (megapixels) |
| Video resolution Information about the maximum resolution at which the rear camera can shoot videos. | 320 x 240 pixels 0.08 MP (megapixels) |
| Features Information about additional software and hardware features of the rear camera which improve its overall performance. | Digital zoom |
Audio
Information about the type of speakers and the audio technologies supported by the device.
| Speaker The loudspeaker is a device, which reproduces various sounds such as ring tones, alarms, music, voice calls, etc. Information about the type of speakers the device uses. | Loudspeaker |
Radio
The radio in a mobile device is a built-in FM radio receiver.
| Radio Information whether the device has an FM radio receiver or not. | No |
Tracking/Positioning
Information about the positioning and navigation technologies supported by the device.
| Tracking/Positioning The tracking/positioning service is provided by various satellite navigation systems, which track the autonomous geo-spatial positioning of the device that supports them. The most common satellite navigation systems are the GPS and the GLONASS. There are also non-satellite technologies for locating mobile devices such as the Enhanced Observed Time Difference, Enhanced 911, GSM Cell ID. | GPS A-GPS |
Wi-Fi
Wi-Fi is a technology that provides wireless data connections between various devices within a short range.
| Wi-Fi Wi-Fi communication between devices is realized via the IEEE 802.11 standards. Some devices have the possibility to serve as Wi-Fi Hotspots by providing internet access for other nearby devices. Wi-Fi Direct (Wi-Fi P2P) is another useful standard that allows devices to communicate with each other without the need for wireless access point (WAP). | 802.11b (IEEE 802.11b-1999) 802.11g (IEEE 802.11g-2003) |
Bluetooth
Bluetooth is a standard for secure wireless data transfer between different types of devices over short distances.
| Version The technology has several versions, which improve the connection speed, range, connectivity and discoverability of the devices. Information about the Bluetooth version of the device. | 2.0 |
| Features Bluetooth uses various profiles and protocols related to faster exchange of data, energy saving, better device discoverability, etc. Some of those supported by the device are listed here. | A2DP (Advanced Audio Distribution Profile) |
USB
The Universal Serial Bus (USB) is an industry standard that allows different electronic devices to exchange data.
| Connector type There are several USB connector types: the Standard one, the Mini and Micro connectors, On-The-Go connectors, etc. Type of the USB connector used by the device. | Micro USB |
| Version There are several versions of the Universal Serial Bus (USB) standard: USB 1.0 (1996), the USB 2.0 (2000), the USB 3.0 (2008), etc. With each following version the rate of data transfer is increased. | 2.0 |
Headphone jack
The headphone jack is an audio phone connector, a.k.a. an audio jack. The most widely used one in mobile devices is the 3.5 mm headphone jack.
| Headphone jack Information whether the device is equipped with a 3.5 mm audio jack. | Yes |
Connectivity
Information about other important connectivity technologies supported by the devices.
| Connectivity Information about some of the most widely used connectivity technologies supported by the device. | Computer sync |
Browser
A web browser is a software application for accessing, fetching, displaying and navigating through information on the World Wide Web.
| Browser Information about some of the features and standards supported by the browser of the device. | HTML xHTML WAP 2.0 |
Audio file formats/codecs
Mobile devices support various audio file formats and codecs, which respectively store and code/decode digital audio data.
| Audio file formats/codecs List of some of the most common audio file formats and codecs supported standardly by the device. | AAC (Advanced Audio Coding) AMR / AMR-NB / GSM-AMR (Adaptive Multi-Rate, .amr, .3ga) MIDI MP3 (MPEG-2 Audio Layer II, .mp3) WMA (Windows Media Audio, .wma) WAV (Waveform Audio File Format, .wav, .wave) |
Video file formats/codecs
Mobile devices support various video file formats and codecs, which respectively store and code/decode digital video data.
| Video file formats/codecs List of some of the most common video file formats and codecs supported standardly by the device. | 3GPP (3rd Generation Partnership Project, .3gp) AVI (Audio Video Interleaved, .avi) MPEG-4 |
Battery
The batteries of mobile devices differ in capacity and technology. They provide the electrical charge needed for the functioning of the devices.
| Capacity The capacity of a battery shows the maximum charge, which it can store, measured in mili-Ampere hours. | 1590 mAh (milliampere-hours) |
| Type The battery type is determined by its structure and more specifically, by the chemicals used in it. There are different battery types and some of the most commonly used in mobile devices are the lithium-ion (Li-Ion) and the lithium-ion polymer battery (Li-Polymer). | Li-Polymer |
| 2G talk time 2G talk time is the time period a battery charge will last, if one is constantly talking on the phone in a 2G cellular network. | 5 hours 50 minutes 5.8 h (hours) 349.8 min (minutes) 0.2 days |
| 2G stand-by time 2G stand-by time is the longest time a battery charge will last, if the device is not used but is constantly connected to the 2G cellular network. | 422 h (hours) 25320 min (minutes) 17.6 days |
| 3G talk time 3G talk time is the time period a battery charge will last, if one is constantly talking on the phone in a 3G cellular network. | 5 hours 10 minutes 5.2 h (hours) 310.2 min (minutes) 0.2 days |
| 3G stand-by time 3G stand-by time is the longest time a battery charge will last, if the device is not used but is constantly connected to the 3G mobile network. | 355 h (hours) 21300 min (minutes) 14.8 days |
| Features Information about some additional features of the device's battery. | Removable |
Additional features
Some devices have additional features, different from the standard ones above, but equally important and worth mentioning.
| Additional features Information about other features of the device. | QWERTY keyboard |